How to Calculate Your Electricity Bill - A Comprehensive Guide
Imagine tiny particles called electrons. These little guys move around things like wires. When we make them move in a specific way, we create electricity.

What is Electricity?
Imagine tiny particles called electrons. These little guys move around things like wires. When we make them move in a specific way, we create electricity. It's like a super-fast, invisible flow of energy. We use electricity to power things like lights, computers, and appliances. It's the reason your phone charges and your TV turns on.
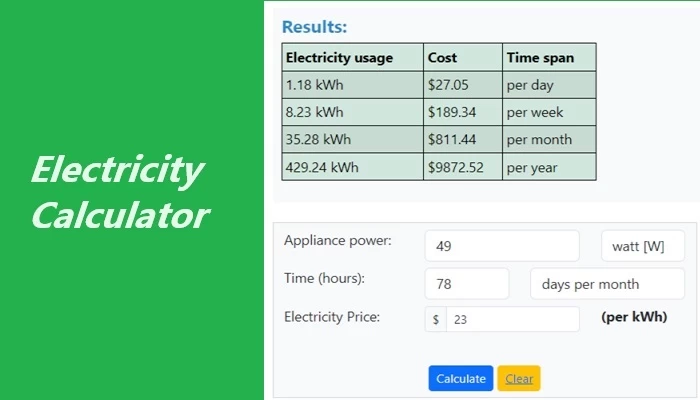
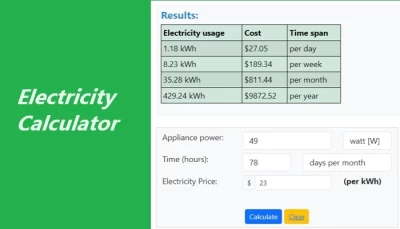
Electricity Calculator
This is a tool that helps you figure out how much electricity you're using and how much it costs. When you plug-in something like your computer, it uses a certain amount of electricity. The calculator helps you understand how much by measuring in units like kilowatt-hours (kWh). It also tells you how much you're paying for that electricity. So, you know the energy your devices use and the cost per unit. In that case, the calculator helps you manage and understand your electricity usage and bill.
Units of Electricity
Electricity is quantified using various units designed to measure different aspects. One widely used unit is the watt (W). Additionally, there are other units such as kilowatts (kW), British Thermal Units (BTU), Horsepower (hp), and tons.
Watts, denoted as W, measure the rate at which energy is transferred, akin to expressing 1 joule per second. A kilowatt is a larger scale than a watt. Breaking it down further, one kilowatt (kW) is equivalent to 1000 watts. Both watts and kilowatts are commonly employed when discussing power.
When it comes to measuring energy, kilowatt-hours (kWh) come into play. A kilowatt-hour signifies the energy required to sustain one kilowatt of power for one hour. In discussions about electricity costs, kilowatt-hours are frequently used. The relationship between energy (E) and power (P) is expressed as P = E / t.
Typically, we measure and pay for electricity in terms of kilowatt-hours due to its simplicity. Describing the energy consumption of an average U.S. household in terms of watts would involve a large number, making it more practical to use kilowatt-hours instead.
Energy Saving Tips
Here are some ways to save energy and lower your electricity bills. Trying out a few of these can make a big difference.
- Watch How You Use Energy
Pay attention to how you use electricity calculator in your daily life. Turn off lights and appliances when you're not using them. Use a fan instead of air conditioning when you can. Wear more clothes and use less heat. Wash smaller loads of laundry and dishes. Small changes add up.
- Switch to LED Bulbs
Replace old bulbs with LED ones. They cost more upfront, but they use less energy. For example, a regular bulb needs 75 watts, but an LED only needs 9 watts. It's an investment that saves you money in the long run.
- Get a Programmable Thermostat
If you can, install a thermostat you can program. A big chunk of energy use comes from heating or cooling. Adjusting the temperature based on when you need it can save a lot of time. You don't need a fancy smart thermostat; even a simple programmable one helps.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances
When buying new appliances, think about energy efficiency. It might cost more, but it pays off over time with lower bills. Consider the long-term cost, not just the price tag.
- Check Your Windows
If you're in a cold area, make sure your windows are energy-efficient to keep the heat inside. In hot places, look for windows that reflect sunlight to keep your home cool. Use curtains or blinds during the brightest parts of the day to save on cooling.
- Insulate Your Home
Make sure your home is well-insulated. This includes windows, doors, vents, attic, walls, floors, basement, and crawl space. Poor insulation makes your heating and cooling systems work harder, costing you more money.

What is Electricity?
Imagine tiny particles called electrons. These little guys move around things like wires. When we make them move in a specific way, we create electricity. It's like a super-fast, invisible flow of energy. We use electricity to power things like lights, computers, and appliances. It's the reason your phone charges and your TV turns on.
Electricity Calculator
This is a tool that helps you figure out how much electricity you're using and how much it costs. When you plug-in something like your computer, it uses a certain amount of electricity. The calculator helps you understand how much by measuring in units like kilowatt-hours (kWh). It also tells you how much you're paying for that electricity. So, you know the energy your devices use and the cost per unit. In that case, the calculator helps you manage and understand your electricity usage and bill.
Units of Electricity
Electricity is quantified using various units designed to measure different aspects. One widely used unit is the watt (W). Additionally, there are other units such as kilowatts (kW), British Thermal Units (BTU), Horsepower (hp), and tons.
Watts, denoted as W, measure the rate at which energy is transferred, akin to expressing 1 joule per second. A kilowatt is a larger scale than a watt. Breaking it down further, one kilowatt (kW) is equivalent to 1000 watts. Both watts and kilowatts are commonly employed when discussing power.
When it comes to measuring energy, kilowatt-hours (kWh) come into play. A kilowatt-hour signifies the energy required to sustain one kilowatt of power for one hour. In discussions about electricity costs, kilowatt-hours are frequently used. The relationship between energy (E) and power (P) is expressed as P = E / t.
Typically, we measure and pay for electricity in terms of kilowatt-hours due to its simplicity. Describing the energy consumption of an average U.S. household in terms of watts would involve a large number, making it more practical to use kilowatt-hours instead.
Energy Saving Tips
Here are some ways to save energy and lower your electricity bills. Trying out a few of these can make a big difference.
- Watch How You Use Energy
Pay attention to how you use electricity calculator in your daily life. Turn off lights and appliances when you're not using them. Use a fan instead of air conditioning when you can. Wear more clothes and use less heat. Wash smaller loads of laundry and dishes. Small changes add up.
- Switch to LED Bulbs
Replace old bulbs with LED ones. They cost more upfront, but they use less energy. For example, a regular bulb needs 75 watts, but an LED only needs 9 watts. It's an investment that saves you money in the long run.
- Get a Programmable Thermostat
If you can, install a thermostat you can program. A big chunk of energy use comes from heating or cooling. Adjusting the temperature based on when you need it can save a lot of time. You don't need a fancy smart thermostat; even a simple programmable one helps.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances
When buying new appliances, think about energy efficiency. It might cost more, but it pays off over time with lower bills. Consider the long-term cost, not just the price tag.
- Check Your Windows
If you're in a cold area, make sure your windows are energy-efficient to keep the heat inside. In hot places, look for windows that reflect sunlight to keep your home cool. Use curtains or blinds during the brightest parts of the day to save on cooling.
- Insulate Your Home
Make sure your home is well-insulated. This includes windows, doors, vents, attic, walls, floors, basement, and crawl space. Poor insulation makes your heating and cooling systems work harder, costing you more money.
Conversation
Latest Blogs
© Blog CoolCalculator, Explore CoolCalculator, your destination for the latest insights, tips, and updates on the world of online calculators. Stay informed and make your calculations smarter with our blog. ,
Designed
by Saad Media Team , Team Lead M.Rizwan Akhtar