Leading Causes of Hyperglycemia and Its Treatments
High blood sugar happens when there’s too much sugar in your blood. It is a key concern, particularly for people with diabetes.
High blood sugar happens when there’s too much sugar in your blood. It is a key concern, particularly for people with diabetes, but it can also affect those without the condition in certain circumstances. Maintaining proper blood glucose levels prevents complications like cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and organ failure. Understanding the causes of hyperglycemia is vital to managing and treating the conditions effectively.
Main Causes of Hyperglycemia
-
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is a disease that makes it hard for your body to use sugar (glucose) for energy. This can cause too much sugar in your blood, which is called high blood sugar. Sometimes, your body doesn’t make enough of a particular hormone called insulin or doesn’t use it well. Insulin helps sugar get into your cells. When there’s not enough insulin, sugar builds up in your blood.
-
Insufficient Insulin or Medication
For people with diabetes, not taking the correct dose of insulin or oral medications can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Skipping medication doses or incorrect administration, like improper insulin injection techniques, can prevent glucose from being adequately managed in the body.
-
Dietary Choices
Consuming foods high in simple sugars and carbohydrates without balancing insulin levels or glucose-lowering medications can cause spikes in blood sugar. Large meals, mainly those rich in processed carbs or sugary foods, contribute to hyperglycemia. Additionally, alcohol consumption, especially in excess, can disrupt blood sugar levels.
-
Stress
When we feel stressed, our bodies make a special kind of juice to increase our blood sugar. These hormones tell our liver to make more sugar. So, if you’re already having trouble with high blood sugar, stress can worsen it.
-
Lack of Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps muscles use glucose for energy, lowering blood sugar levels. A sedentary lifestyle or sudden reduction in physical activity can prevent the body from utilizing glucose efficiently, contributing to hyperglycemia.
-
Infections and Illness
When you get sick or have an infection, your body makes special chemicals to raise your blood sugar.
-
Hormonal Changes
Some health problems, like PCOS, Cushing’s syndrome, and issues with your hormones, can make it hard for your body to use insulin. This can make your blood sugar go up. When women are pregnant, their hormones can change and cause gestational diabetes, which can also make their blood sugar go up.
Treatments for Hyperglycemia
Managing hyperglycemia involves lifestyle changes, medications, and ongoing monitoring. The treatment varies depending on whether the person has diabetes or is experiencing transient hyperglycemia due to other factors.
-
Insulin Therapy
Some people with Type 1 diabetes or high blood sugar need insulin shots. Insulin helps keep their blood sugar from getting too high. The amount of insulin they take depends on their blood sugar, what they eat, and how much they move around.
-
Oral Medications
People with Type 2 diabetes might be given pills like metformin or sulfonylurea’s. These medicines help the body use insulin better or make the pancreas produce more insulin.
-
Dietary Modifications
Managing carbohydrate intake, opting for complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, and reducing sugary and processed foods can prevent blood sugar spikes. Therefore, eating a variety of foods is essential. You should eat many vegetables, lean meats like chicken or fish, and healthy oils.
-
Regular Exercise
When you move around, your body gets better at using the insulin it makes to turn sugar into energy. This helps keep your blood sugar from getting too high. Regularly incorporating moderate exercise, such as walking or cycling, is essential for managing hyperglycemia.
-
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood glucose monitoring allows individuals to track their levels and adjust their treatment plans. This is crucial for early intervention and prevention of sever hyperglycemia.
-
Stress Management
Stress can make your blood sugar go up. Doing things like deep breathing, meditation, or talking to a counselor can help you feel less stressed. This can also help keep your blood sugar from going too high.
-
Treatment of Underlying Causes
If hyperglycemia is caused by an underlying infection, hormonal disorder, or medication side effects, addressing these conditions is crucial for long-term management.
Important Aspects Related to Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, occurs when excessive glucose is in the bloodstream. This condition is mainly associated with diabetes, but several factors contribute to its onset. Understanding these causes and recognizing the symptoms is critical for proper management and treatment.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
The main reasons for high blood sugar are either the pancreas not making enough insulin or the body not using insulin correctly. Insulin helps keep blood sugar levels steady. The immune system is like anybody’s army which helps fight off bad things. But sometimes, it makes a mistake and attacks the wrong part of the body. The immune system is like a bodyguard that protects us from bad things.
In type 1 diabetes, the bodyguard attacks the wrong part of the body. It attacks the part of the pancreas that makes insulin. Insulin is a specific juice that helps the body use sugar for energy. When the pancreas can’t make enough insulin, the body can’t use sugar properly. Diabetes is when the immune system attacks the body’s tissues. People with type 2 diabetes have a hard time using insulin, even though their body makes it. This is called insulin resistance.
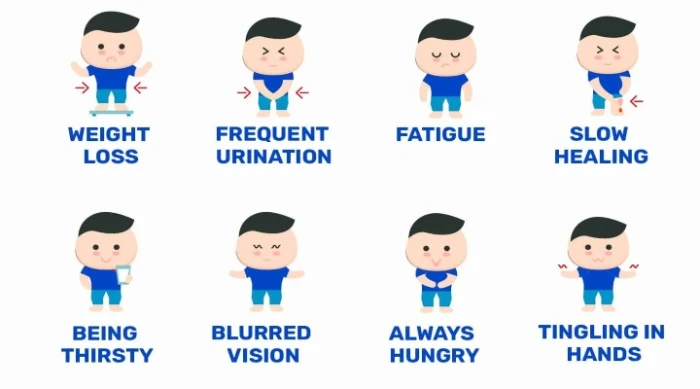
Acute Hyperglycemia Symptoms
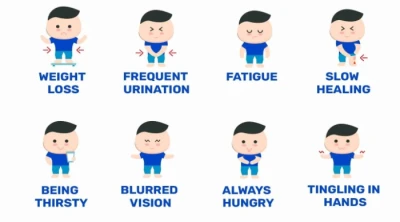
High blood sugar can happen quickly and cause problems. You might feel thirsty, need to pee a lot, be tired, see blurry, and have headaches. If it’s not treated, it can get worse and cause severe problems like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This is when your body uses fat for energy instead of sugar, which makes harmful acids in your blood. In bad cases, you might get a Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS), which is dangerous. High blood sugar can also damage your heart, kidneys, and nerves over time.
Difference between Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are both problems with blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia means your blood sugar is too low, which can happen if you take too much insulin or skip meals. Hyperglycemia means your blood sugar is too high, which can occur if you don’t have enough insulin.
Autoimmune Diseases
Some autoimmune diseases, like type 1 diabetes, can cause high blood sugar. People with type 1 diabetes have a problem with their body. Their body’s defense system (immune system) mistakenly attacks the insulin cells, a particular substance that helps control blood sugar levels. Other autoimmune diseases, like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, can also affect blood sugar levels, but in a different way. They can change how the body uses sugar.
People with high blood sugar need different treatments depending on their blood sugar levels. If you have type 1 diabetes, you need to take insulin every day to keep your blood sugar under control. If you have type 1 diabetes, you can often manage it by eating healthy food, exercising more, and taking medicine that helps your body use insulin better. Sometimes, people with type 2 diabetes also need to take insulin. It’s essential to check your blood sugar often and watch for signs of problems to prevent complications.
Hyperglycemia is a big problem for people with diabetes. It means their blood sugar is too high. They need to know what causes it and take good care of themselves to keep it under control. This includes taking medicine, eating healthy, exercising, and checking their blood sugar often. If you don’t control your blood sugar well, it can cause problems later on. But there are ways to stay healthy and happy even with diabetes.
High blood sugar happens when there’s too much sugar in your blood. It is a key concern, particularly for people with diabetes, but it can also affect those without the condition in certain circumstances. Maintaining proper blood glucose levels prevents complications like cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and organ failure. Understanding the causes of hyperglycemia is vital to managing and treating the conditions effectively.
Main Causes of Hyperglycemia
-
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is a disease that makes it hard for your body to use sugar (glucose) for energy. This can cause too much sugar in your blood, which is called high blood sugar. Sometimes, your body doesn’t make enough of a particular hormone called insulin or doesn’t use it well. Insulin helps sugar get into your cells. When there’s not enough insulin, sugar builds up in your blood.
-
Insufficient Insulin or Medication
For people with diabetes, not taking the correct dose of insulin or oral medications can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Skipping medication doses or incorrect administration, like improper insulin injection techniques, can prevent glucose from being adequately managed in the body.
-
Dietary Choices
Consuming foods high in simple sugars and carbohydrates without balancing insulin levels or glucose-lowering medications can cause spikes in blood sugar. Large meals, mainly those rich in processed carbs or sugary foods, contribute to hyperglycemia. Additionally, alcohol consumption, especially in excess, can disrupt blood sugar levels.
-
Stress
When we feel stressed, our bodies make a special kind of juice to increase our blood sugar. These hormones tell our liver to make more sugar. So, if you’re already having trouble with high blood sugar, stress can worsen it.
-
Lack of Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps muscles use glucose for energy, lowering blood sugar levels. A sedentary lifestyle or sudden reduction in physical activity can prevent the body from utilizing glucose efficiently, contributing to hyperglycemia.
-
Infections and Illness
When you get sick or have an infection, your body makes special chemicals to raise your blood sugar.
-
Hormonal Changes
Some health problems, like PCOS, Cushing’s syndrome, and issues with your hormones, can make it hard for your body to use insulin. This can make your blood sugar go up. When women are pregnant, their hormones can change and cause gestational diabetes, which can also make their blood sugar go up.
Treatments for Hyperglycemia
Managing hyperglycemia involves lifestyle changes, medications, and ongoing monitoring. The treatment varies depending on whether the person has diabetes or is experiencing transient hyperglycemia due to other factors.
-
Insulin Therapy
Some people with Type 1 diabetes or high blood sugar need insulin shots. Insulin helps keep their blood sugar from getting too high. The amount of insulin they take depends on their blood sugar, what they eat, and how much they move around.
-
Oral Medications
People with Type 2 diabetes might be given pills like metformin or sulfonylurea’s. These medicines help the body use insulin better or make the pancreas produce more insulin.
-
Dietary Modifications
Managing carbohydrate intake, opting for complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, and reducing sugary and processed foods can prevent blood sugar spikes. Therefore, eating a variety of foods is essential. You should eat many vegetables, lean meats like chicken or fish, and healthy oils.
-
Regular Exercise
When you move around, your body gets better at using the insulin it makes to turn sugar into energy. This helps keep your blood sugar from getting too high. Regularly incorporating moderate exercise, such as walking or cycling, is essential for managing hyperglycemia.
-
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood glucose monitoring allows individuals to track their levels and adjust their treatment plans. This is crucial for early intervention and prevention of sever hyperglycemia.
-
Stress Management
Stress can make your blood sugar go up. Doing things like deep breathing, meditation, or talking to a counselor can help you feel less stressed. This can also help keep your blood sugar from going too high.
-
Treatment of Underlying Causes
If hyperglycemia is caused by an underlying infection, hormonal disorder, or medication side effects, addressing these conditions is crucial for long-term management.
Important Aspects Related to Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, occurs when excessive glucose is in the bloodstream. This condition is mainly associated with diabetes, but several factors contribute to its onset. Understanding these causes and recognizing the symptoms is critical for proper management and treatment.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
The main reasons for high blood sugar are either the pancreas not making enough insulin or the body not using insulin correctly. Insulin helps keep blood sugar levels steady. The immune system is like anybody’s army which helps fight off bad things. But sometimes, it makes a mistake and attacks the wrong part of the body. The immune system is like a bodyguard that protects us from bad things.
In type 1 diabetes, the bodyguard attacks the wrong part of the body. It attacks the part of the pancreas that makes insulin. Insulin is a specific juice that helps the body use sugar for energy. When the pancreas can’t make enough insulin, the body can’t use sugar properly. Diabetes is when the immune system attacks the body’s tissues. People with type 2 diabetes have a hard time using insulin, even though their body makes it. This is called insulin resistance.
Acute Hyperglycemia Symptoms
High blood sugar can happen quickly and cause problems. You might feel thirsty, need to pee a lot, be tired, see blurry, and have headaches. If it’s not treated, it can get worse and cause severe problems like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This is when your body uses fat for energy instead of sugar, which makes harmful acids in your blood. In bad cases, you might get a Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS), which is dangerous. High blood sugar can also damage your heart, kidneys, and nerves over time.
Difference between Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are both problems with blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia means your blood sugar is too low, which can happen if you take too much insulin or skip meals. Hyperglycemia means your blood sugar is too high, which can occur if you don’t have enough insulin.
Autoimmune Diseases
Some autoimmune diseases, like type 1 diabetes, can cause high blood sugar. People with type 1 diabetes have a problem with their body. Their body’s defense system (immune system) mistakenly attacks the insulin cells, a particular substance that helps control blood sugar levels. Other autoimmune diseases, like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, can also affect blood sugar levels, but in a different way. They can change how the body uses sugar.
People with high blood sugar need different treatments depending on their blood sugar levels. If you have type 1 diabetes, you need to take insulin every day to keep your blood sugar under control. If you have type 1 diabetes, you can often manage it by eating healthy food, exercising more, and taking medicine that helps your body use insulin better. Sometimes, people with type 2 diabetes also need to take insulin. It’s essential to check your blood sugar often and watch for signs of problems to prevent complications.
Hyperglycemia is a big problem for people with diabetes. It means their blood sugar is too high. They need to know what causes it and take good care of themselves to keep it under control. This includes taking medicine, eating healthy, exercising, and checking their blood sugar often. If you don’t control your blood sugar well, it can cause problems later on. But there are ways to stay healthy and happy even with diabetes.
Conversation
Latest Blogs
© Blog CoolCalculator, Explore CoolCalculator, your destination for the latest insights, tips, and updates on the world of online calculators. Stay informed and make your calculations smarter with our blog. ,
Designed
by Saad Media Team , Team Lead M.Rizwan Akhtar