The Complete Guide to Health, Wellness, and Peak Performance
Explore the risks of high blood pressure, kidney problems, and osteoporosis, and unlock your peak performance potential for a healthier, happier you.

What is Fitness?
Fitness is all about being healthy and strong. It means your body can do activities without feeling too tired. When you're fit, your heart works well, your muscles are strong, and you have good energy. Staying fit is important because it helps our bodies work better and keeps us healthy. When we exercise regularly and eat well, our muscles and organs become stronger, and our immune system gets a boost. Being fit also gives us more energy to do the things we enjoy, like playing with friends, going for a walk, or even just feeling good in our skin. It's like giving our body a gift - a gift that keeps us happy and ready for whatever life brings our way. So, staying fit isn't just about looking good; it's about feeling good and living a better, happier life.
Different Factors of Fitness
-
Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance assesses the effectiveness of the coordination between the heart and lungs during physical activity. Participating in pursuits like running, cycling, or swimming contributes to enhancing cardiovascular endurance. Calculators such as the VO2 max test can assess how efficiently your body utilizes oxygen during exercise, providing insights into your cardiovascular fitness level.
-
Muscular Strength
Muscular strength pertains to the capacity of your muscles to generate force. Lifting weights is a common way to build muscular strength. The One-Rep-Max Calculator is a valuable tool for estimating the maximum weight you can lift for a single repetition, offering a quantitative measure of your muscular strength.
-
Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance focuses on how long your muscles can perform repetitive tasks without fatigue. Exercises like push-ups and squats help build muscular endurance over time. While there might not be specific calculators for this factor, tracking the number of repetitions you can complete serves as a practical measure of your muscular endurance progress.
-
Flexibility
Flexibility is the capacity of your joints and muscles to move quickly. Engaging in activities like yoga enhances flexibility.
-
Body Composition
Body composition assesses the ratio of muscle to fat in your body. Body mass index and body fat calculators are commonly used tools to gauge body composition. These calculators provide insights beyond mere weight, offering a more comprehensive understanding of your body's composition.
-
Balance and Coordination
Balance and coordination are essential for smooth movements and injury prevention. Activities like Tai Chi and specific balance exercises contribute to improving these factors.
-
Nutrition
Nutrition is a cornerstone of fitness, influencing energy levels, muscle recovery, and overall well-being. Utilizing nutrition calculators like calorie and calorie-burned calculators can help track your daily intake of calories, protein, carbohydrates, and other essential nutrients. Balancing your diet is vital to providing the necessary fuel for workouts and supporting your body's overall fitness journey.
-
Water Intake
Water intake is super important for fitness because it helps your body do its job correctly. When you work out, you sweat, and that's your body's way of cooling down. If you don't drink enough water, you can get dehydrated, which makes it harder for your muscles to work well. Plus, water helps transport nutrients to your strengths and gets rid of waste. It acts like the fuel that keeps your body's engine running smoothly during exercise. So, make sure to sip on water throughout the day and get help through the water intake calculator, especially when you're active, to keep yourself hydrated and support your overall fitness goals.

Role of Rest and Recovery in Your Fitness Goal
Many individuals prioritize the intensity and frequency of their exercise routines but often overlook the significance of giving the body sufficient time to rest and recover. Here are some critical aspects of the role of rest and recovery in fitness.
Muscle Repair and Growth
During exercise, especially strength training, muscles experience microscopic damage. Rest durations allow the body to repair and rebuild these muscles, leading to growth and increased strength.
Prevention of Overtraining
Overtraining occurs when the intensity and volume of exercise surpass the body's ability to recover. This can lead to fatigue, decreased performance, an increased risk of injury, and even immune system suppression. Adequate rest helps prevent overtraining and promotes overall well-being.
Hormonal Balance
Intense workouts can disrupt hormonal balance, particularly cortisol (a stress hormone) levels. Sufficient rest helps restore hormonal balance, promoting a healthy body environment for muscle growth and recovery.
Injury Prevention
Continuous stress on muscles and joints without proper recovery increases the risk of injuries. Rest days give the body a chance to repair tissues, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of overuse injuries.
Improved Performance
Regular rest and recovery positively impact performance. Athletes often experience enhanced strength, endurance, and overall performance after a period of rest, allowing them to train at higher intensities during subsequent workouts.
Mental Well-Being
Physical activity, especially intense exercise, can place stress on the central nervous system. Adequate rest helps maintain mental well-being by preventing burnout, reducing fatigue, and improving focus and motivation.
Adaptation to Training Stimulus
The body needs time to adapt to the stress of exercise. Recovery allows for the consolidation of training adaptations, ensuring that the body becomes more robust, fitter, and more resilient over time.
Sleep Quality

Quality sleep is a important component of recovery. During the sleep period, the body releases growth hormone, which aids in muscle repair and overall recovery. Poor sleep can hinder these processes and negatively impact fitness goals.
Getting an adequate amount of good-quality sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being. Sleep plays a key role in various physiological and psychological functions, and its effects on the body are extensive. Here are some key ways in which good sleep contributes to a healthy body.
- Physical Restoration
During sleep, the body undergoes repair and maintenance processes. Muscles are tissues are repaired, and the immune system is strengthened, promoting overall physical health.
- Cognitive Function
Quality sleep is important for cognitive functions such as memory consolidation, problem-solving, and learning. It enhances creativity, decision-making, and overall mental sharpness.
- Mood Regulation
Adequate sleep is linked to emotional well-being. It helps regulate mood, reduces stress, and contributes to a more positive outlook on life. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can lead to irritability and heightened emotional reactivity.
- Weight Management
There is a connection between sleep and weight management. The Sleep Cycle Calculator, which analyzes sleep cycles, can help optimize sleep duration and timing. Poor sleep has been associated with an increased risk of obesity and metabolic disorders. Additionally, a Weight Calculator can assist in monitoring and managing body weight. Maintaining a healthy weight is a multifaceted goal, and proper sleep is one of the factors that contribute to overall well-being and weight management.
Nutrient Utilization
Rest days provide an opportunity for the body to effectively utilize nutrients, including protein, for muscle repair and growth. Proper nutrition, combined with rest, maximizes the benefits of training.
Long-Term Sustainability
Incorporating rest and recovery into your fitness routine contributes to long-term sustainability. Balancing intense workouts with adequate rest helps prevent burnout. It allows individuals to maintain a consistent and enjoyable exercise routine over the years.
Metabolic Fitness
Metabolism is a set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. It involves various biochemical processes that convert food into energy, essential for maintaining bodily functions and supporting life. Metabolism can be broadly categorized into two main types - catabolism, which involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy, and anabolism, which encompasses the synthesis of complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy, and anabolism, which encompasses the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
The effect of metabolism on body fitness is profound. A faster metabolism is often associated with a higher calorie-burning rate, aiding in weight management and fat loss. Individuals with a more efficient metabolism may find it easier to maintain a healthy body weight and composition. Regular physical activity can contribute to an increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is the amount of energy expended at rest that can be calculate using a BMR calculator. This highlights the crucial role of exercise in supporting overall metabolic health.
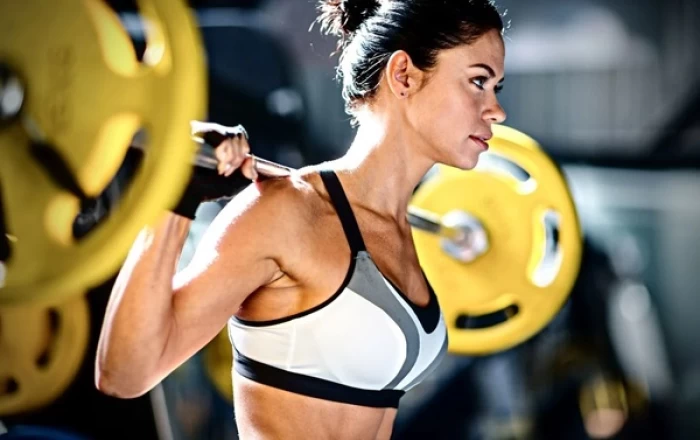

Fitness calculators provide valuable insights into various aspects of metabolism and body fitness. Additionally, the Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator takes into account your activity level to determine the total calories burned throughout the day. Calculators like Body Mass Index (BMI) can also help assess the relationship between weight and height, serving as a general indicator of body composition and potential health risks.
Diet Guidelines to Stay Fit and Healthy
-
Balanced Diet
Eat a variety of foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These give you vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants. According to the World Health Organization, your diet should be about 55-75% carbs, 10-15% protein, and 15-30% fats.
-
Portion Control
Watch how much you eat to avoid overeating. Smaller plates and bowls can help. The American Heart Association suggests the "Healthy Eating Plate" rule - fill half with fruits and veggies, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with whole grains.
-
Hydration
Drink enough water daily. The National Academies say men need about 3.7 liters (125 ounces), and women need 2.7 liters (91 ounces) from all drinks and food.
-
Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
Cut down on processed foods with lots of added sugars, salth, and bad fats. The American Heart Association recommends men have no more than nine teaspoons (38 grams) and women have no more than six teaspoons (25 grams) of added sugars each day.
-
Healthy Fats
Go for good fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. The American Heart Association suggests getting 20-35% of your daily calories from healthy fats. Unhealthy fat should not be put on, so take steps towards removing non-essential fat from your body using a body fat calculator and an ideal weight calculator combined.
-
Regular Physical Activity
Do at least 150 minutes of medium-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of strenuous exercise each week, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
-
Meal Timing
Stick to a regular meal schedule to help your metabolism. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics recommends three meals and one to two snacks a day.
-
Limit Salt Intake
Excessive consumption of table salt, or sodium chloride, can have various adverse effects on health. The recommended daily intake of salt varies by country and health organization. Still, it is generally advised to limit salt intake to about 2,300 milligrams(mg) per day for adults, with an ideal target of 1,500 mg for specific populations, such as those with high blood pressure, older adults, and African Americans.
What Are the Health Risks of Table Salt?
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
One of the most well-established links between excessive salt intake and health issues is an increased risk of high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
Cardiovascular Disease
Excessive salt intake has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. High blood pressure, which can be caused or exacerbated by high salt intake, puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Kidney Problems
Too much salt can strain the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney problems over time. Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions may be particularly vulnerable.
Fluid Retention
Salt has the ability to retain water in the body, leading to fluid retention. This can contribute to swelling (edema), particularly in the extremities.
Osteoporosis
Some studies suggest a link between high salt intake and increased calcium loss through urine, which may contribute to a higher risk of osteoporosis.
Stomach Cancer
There is evidence suggesting that a high-salt diet may be associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer, particularly for those infected with Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium linked to stomach ulcers and cancer.
It's important to note that the majority of the salt in our diet comes from processed and packaged foods rather than the salt we add while cooking or at the table. Therefore, being mindful of processed food intake and choosing low-sodium alternatives can be beneficial in reducing overall salt consumption.
Role of Early Rising in Health and Fitness
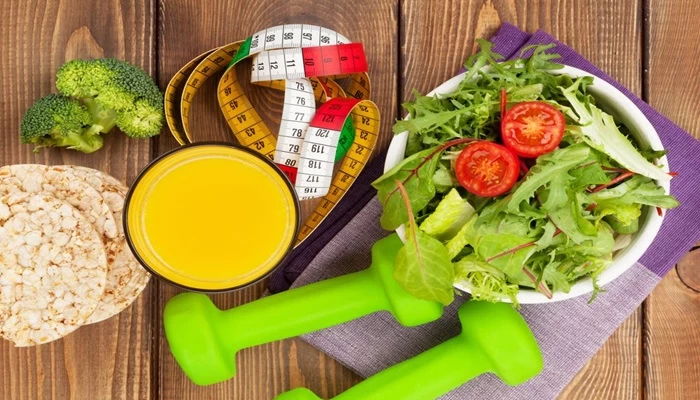

Waking up early plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. The first rays of the morning sun bring with them a myriad of benefits for our overall well-being. Rising early aligns our body with the natural circadian rhythm, promoting a sense of balance and harmony.
Early mornings offer a chance to partake in physical activities that promote fitness. Be it a brisk walk, a jog, or a rejuvenating yoga session, the serenity of dawn amplifies the overall experience, rendering it not only more pleasant but also revitalizing. The stillness of the early hours establishes a tranquil backdrop, fostering a serene atmosphere conducive to focused and mindful exercise. This sets a positive tone for the day and encourages a healthy start. Utilizing a pace calculator during these activities can further enhance your fitness routine by providing valuable insights into your performance and progress.
Moreover, the cooler temperatures in the early morning are conducive to effective workouts. The body is more responsive to physical exertion, and the fresh air aids in oxygenating the cells, enhancing stamina and endurance. This can lead to a more effective and efficient fitness routine, as the body is primed to perform at its best.
Early rising also provides an opportunity for a nourishing breakfast, a crucial aspect of a healthy lifestyle. A well-balanced breakfast kick starts the metabolism, ensuring that the body efficiently utilizes energy throughout the day. This, in turn, contributes to weight management and overall fitness.
In addition to the physical benefits, early mornings offer a quiet and undisturbed time for mental well-being. Moments of solitude in the morning can be used for meditation, reflection, or to set positive intentions for the day ahead. This mental clarity and focus acquired in the early hours can positively impact decision-making, stress management, and emotional resilience.

What is Fitness?
Fitness is all about being healthy and strong. It means your body can do activities without feeling too tired. When you're fit, your heart works well, your muscles are strong, and you have good energy. Staying fit is important because it helps our bodies work better and keeps us healthy. When we exercise regularly and eat well, our muscles and organs become stronger, and our immune system gets a boost. Being fit also gives us more energy to do the things we enjoy, like playing with friends, going for a walk, or even just feeling good in our skin. It's like giving our body a gift - a gift that keeps us happy and ready for whatever life brings our way. So, staying fit isn't just about looking good; it's about feeling good and living a better, happier life.
Different Factors of Fitness
-
Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance assesses the effectiveness of the coordination between the heart and lungs during physical activity. Participating in pursuits like running, cycling, or swimming contributes to enhancing cardiovascular endurance. Calculators such as the VO2 max test can assess how efficiently your body utilizes oxygen during exercise, providing insights into your cardiovascular fitness level.
-
Muscular Strength
Muscular strength pertains to the capacity of your muscles to generate force. Lifting weights is a common way to build muscular strength. The One-Rep-Max Calculator is a valuable tool for estimating the maximum weight you can lift for a single repetition, offering a quantitative measure of your muscular strength.
-
Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance focuses on how long your muscles can perform repetitive tasks without fatigue. Exercises like push-ups and squats help build muscular endurance over time. While there might not be specific calculators for this factor, tracking the number of repetitions you can complete serves as a practical measure of your muscular endurance progress.
-
Flexibility
Flexibility is the capacity of your joints and muscles to move quickly. Engaging in activities like yoga enhances flexibility.
-
Body Composition
Body composition assesses the ratio of muscle to fat in your body. Body mass index and body fat calculators are commonly used tools to gauge body composition. These calculators provide insights beyond mere weight, offering a more comprehensive understanding of your body's composition.
-
Balance and Coordination
Balance and coordination are essential for smooth movements and injury prevention. Activities like Tai Chi and specific balance exercises contribute to improving these factors.
-
Nutrition
Nutrition is a cornerstone of fitness, influencing energy levels, muscle recovery, and overall well-being. Utilizing nutrition calculators like calorie and calorie-burned calculators can help track your daily intake of calories, protein, carbohydrates, and other essential nutrients. Balancing your diet is vital to providing the necessary fuel for workouts and supporting your body's overall fitness journey.
-
Water Intake
Water intake is super important for fitness because it helps your body do its job correctly. When you work out, you sweat, and that's your body's way of cooling down. If you don't drink enough water, you can get dehydrated, which makes it harder for your muscles to work well. Plus, water helps transport nutrients to your strengths and gets rid of waste. It acts like the fuel that keeps your body's engine running smoothly during exercise. So, make sure to sip on water throughout the day and get help through the water intake calculator, especially when you're active, to keep yourself hydrated and support your overall fitness goals.

Role of Rest and Recovery in Your Fitness Goal
Many individuals prioritize the intensity and frequency of their exercise routines but often overlook the significance of giving the body sufficient time to rest and recover. Here are some critical aspects of the role of rest and recovery in fitness.
Muscle Repair and Growth
During exercise, especially strength training, muscles experience microscopic damage. Rest durations allow the body to repair and rebuild these muscles, leading to growth and increased strength.
Prevention of Overtraining
Overtraining occurs when the intensity and volume of exercise surpass the body's ability to recover. This can lead to fatigue, decreased performance, an increased risk of injury, and even immune system suppression. Adequate rest helps prevent overtraining and promotes overall well-being.
Hormonal Balance
Intense workouts can disrupt hormonal balance, particularly cortisol (a stress hormone) levels. Sufficient rest helps restore hormonal balance, promoting a healthy body environment for muscle growth and recovery.
Injury Prevention
Continuous stress on muscles and joints without proper recovery increases the risk of injuries. Rest days give the body a chance to repair tissues, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of overuse injuries.
Improved Performance
Regular rest and recovery positively impact performance. Athletes often experience enhanced strength, endurance, and overall performance after a period of rest, allowing them to train at higher intensities during subsequent workouts.
Mental Well-Being
Physical activity, especially intense exercise, can place stress on the central nervous system. Adequate rest helps maintain mental well-being by preventing burnout, reducing fatigue, and improving focus and motivation.
Adaptation to Training Stimulus
The body needs time to adapt to the stress of exercise. Recovery allows for the consolidation of training adaptations, ensuring that the body becomes more robust, fitter, and more resilient over time.
Sleep Quality

Quality sleep is a important component of recovery. During the sleep period, the body releases growth hormone, which aids in muscle repair and overall recovery. Poor sleep can hinder these processes and negatively impact fitness goals.
Getting an adequate amount of good-quality sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being. Sleep plays a key role in various physiological and psychological functions, and its effects on the body are extensive. Here are some key ways in which good sleep contributes to a healthy body.
- Physical Restoration
During sleep, the body undergoes repair and maintenance processes. Muscles are tissues are repaired, and the immune system is strengthened, promoting overall physical health.
- Cognitive Function
Quality sleep is important for cognitive functions such as memory consolidation, problem-solving, and learning. It enhances creativity, decision-making, and overall mental sharpness.
- Mood Regulation
Adequate sleep is linked to emotional well-being. It helps regulate mood, reduces stress, and contributes to a more positive outlook on life. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can lead to irritability and heightened emotional reactivity.
- Weight Management
There is a connection between sleep and weight management. The Sleep Cycle Calculator, which analyzes sleep cycles, can help optimize sleep duration and timing. Poor sleep has been associated with an increased risk of obesity and metabolic disorders. Additionally, a Weight Calculator can assist in monitoring and managing body weight. Maintaining a healthy weight is a multifaceted goal, and proper sleep is one of the factors that contribute to overall well-being and weight management.
Nutrient Utilization
Rest days provide an opportunity for the body to effectively utilize nutrients, including protein, for muscle repair and growth. Proper nutrition, combined with rest, maximizes the benefits of training.
Long-Term Sustainability
Incorporating rest and recovery into your fitness routine contributes to long-term sustainability. Balancing intense workouts with adequate rest helps prevent burnout. It allows individuals to maintain a consistent and enjoyable exercise routine over the years.
Metabolic Fitness
Metabolism is a set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. It involves various biochemical processes that convert food into energy, essential for maintaining bodily functions and supporting life. Metabolism can be broadly categorized into two main types - catabolism, which involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy, and anabolism, which encompasses the synthesis of complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy, and anabolism, which encompasses the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input.
The effect of metabolism on body fitness is profound. A faster metabolism is often associated with a higher calorie-burning rate, aiding in weight management and fat loss. Individuals with a more efficient metabolism may find it easier to maintain a healthy body weight and composition. Regular physical activity can contribute to an increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is the amount of energy expended at rest that can be calculate using a BMR calculator. This highlights the crucial role of exercise in supporting overall metabolic health.

Fitness calculators provide valuable insights into various aspects of metabolism and body fitness. Additionally, the Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator takes into account your activity level to determine the total calories burned throughout the day. Calculators like Body Mass Index (BMI) can also help assess the relationship between weight and height, serving as a general indicator of body composition and potential health risks.
Diet Guidelines to Stay Fit and Healthy
-
Balanced Diet
Eat a variety of foods like fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These give you vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants. According to the World Health Organization, your diet should be about 55-75% carbs, 10-15% protein, and 15-30% fats.
-
Portion Control
Watch how much you eat to avoid overeating. Smaller plates and bowls can help. The American Heart Association suggests the "Healthy Eating Plate" rule - fill half with fruits and veggies, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with whole grains.
-
Hydration
Drink enough water daily. The National Academies say men need about 3.7 liters (125 ounces), and women need 2.7 liters (91 ounces) from all drinks and food.
-
Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
Cut down on processed foods with lots of added sugars, salth, and bad fats. The American Heart Association recommends men have no more than nine teaspoons (38 grams) and women have no more than six teaspoons (25 grams) of added sugars each day.
-
Healthy Fats
Go for good fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. The American Heart Association suggests getting 20-35% of your daily calories from healthy fats. Unhealthy fat should not be put on, so take steps towards removing non-essential fat from your body using a body fat calculator and an ideal weight calculator combined.
-
Regular Physical Activity
Do at least 150 minutes of medium-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of strenuous exercise each week, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
-
Meal Timing
Stick to a regular meal schedule to help your metabolism. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics recommends three meals and one to two snacks a day.
-
Limit Salt Intake
Excessive consumption of table salt, or sodium chloride, can have various adverse effects on health. The recommended daily intake of salt varies by country and health organization. Still, it is generally advised to limit salt intake to about 2,300 milligrams(mg) per day for adults, with an ideal target of 1,500 mg for specific populations, such as those with high blood pressure, older adults, and African Americans.
What Are the Health Risks of Table Salt?
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
One of the most well-established links between excessive salt intake and health issues is an increased risk of high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
Cardiovascular Disease
Excessive salt intake has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. High blood pressure, which can be caused or exacerbated by high salt intake, puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Kidney Problems
Too much salt can strain the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney problems over time. Individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions may be particularly vulnerable.
Fluid Retention
Salt has the ability to retain water in the body, leading to fluid retention. This can contribute to swelling (edema), particularly in the extremities.
Osteoporosis
Some studies suggest a link between high salt intake and increased calcium loss through urine, which may contribute to a higher risk of osteoporosis.
Stomach Cancer
There is evidence suggesting that a high-salt diet may be associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer, particularly for those infected with Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium linked to stomach ulcers and cancer.
It's important to note that the majority of the salt in our diet comes from processed and packaged foods rather than the salt we add while cooking or at the table. Therefore, being mindful of processed food intake and choosing low-sodium alternatives can be beneficial in reducing overall salt consumption.
Role of Early Rising in Health and Fitness

Waking up early plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. The first rays of the morning sun bring with them a myriad of benefits for our overall well-being. Rising early aligns our body with the natural circadian rhythm, promoting a sense of balance and harmony.
Early mornings offer a chance to partake in physical activities that promote fitness. Be it a brisk walk, a jog, or a rejuvenating yoga session, the serenity of dawn amplifies the overall experience, rendering it not only more pleasant but also revitalizing. The stillness of the early hours establishes a tranquil backdrop, fostering a serene atmosphere conducive to focused and mindful exercise. This sets a positive tone for the day and encourages a healthy start. Utilizing a pace calculator during these activities can further enhance your fitness routine by providing valuable insights into your performance and progress.
Moreover, the cooler temperatures in the early morning are conducive to effective workouts. The body is more responsive to physical exertion, and the fresh air aids in oxygenating the cells, enhancing stamina and endurance. This can lead to a more effective and efficient fitness routine, as the body is primed to perform at its best.
Early rising also provides an opportunity for a nourishing breakfast, a crucial aspect of a healthy lifestyle. A well-balanced breakfast kick starts the metabolism, ensuring that the body efficiently utilizes energy throughout the day. This, in turn, contributes to weight management and overall fitness.
In addition to the physical benefits, early mornings offer a quiet and undisturbed time for mental well-being. Moments of solitude in the morning can be used for meditation, reflection, or to set positive intentions for the day ahead. This mental clarity and focus acquired in the early hours can positively impact decision-making, stress management, and emotional resilience.
Conversation
Latest Blogs
© Blog CoolCalculator, Explore CoolCalculator, your destination for the latest insights, tips, and updates on the world of online calculators. Stay informed and make your calculations smarter with our blog. ,
Designed
by Saad Media Team , Team Lead M.Rizwan Akhtar